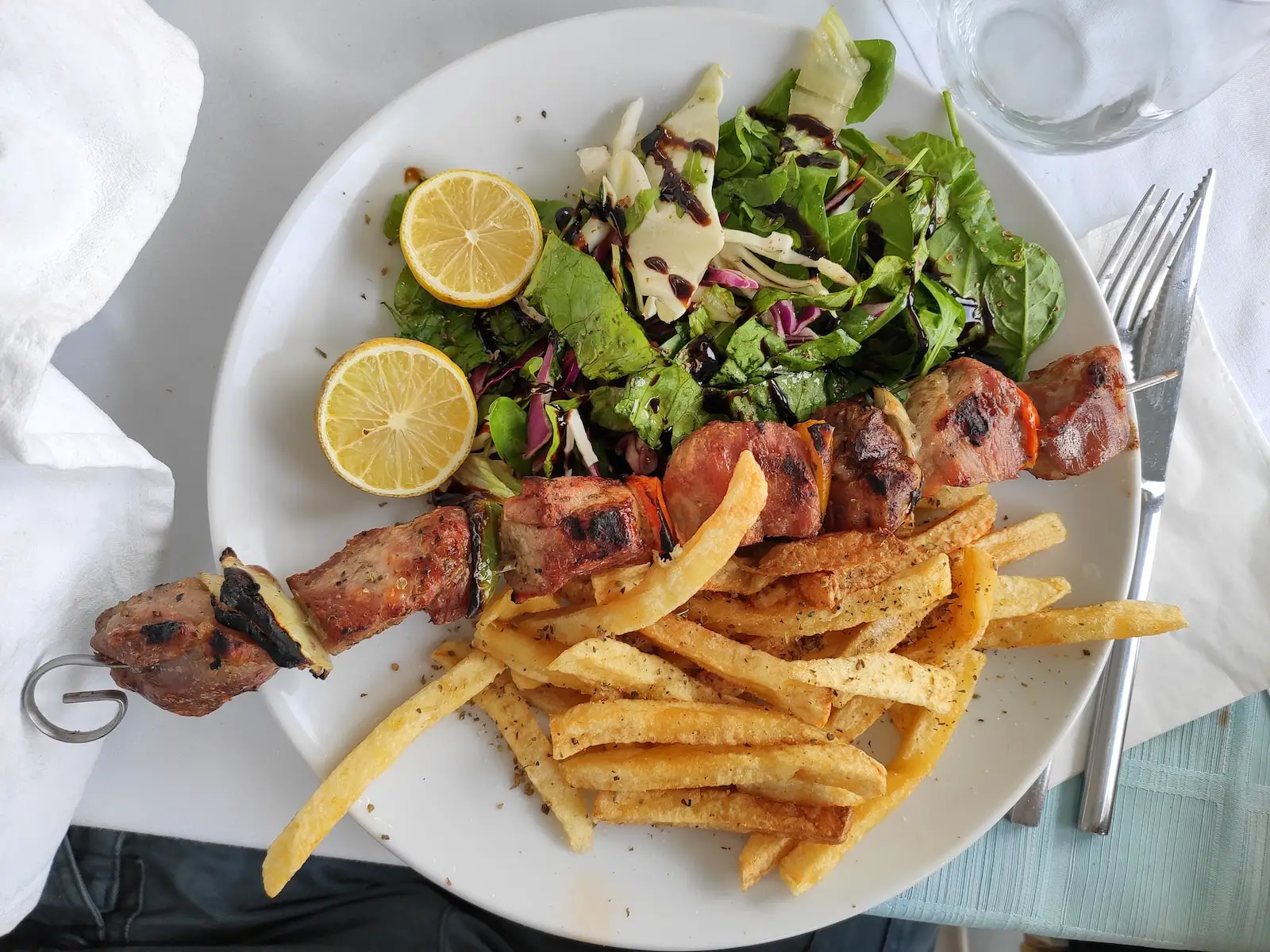Souvlaki and gyro are both popular Greek dishes, but they differ in preparation, ingredients, and presentation.
- Souvlaki:
- Ingredients: Souvlaki typically consists of small pieces of meat and sometimes vegetables grilled on a skewer. It can be made with a variety of meats, including chicken, pork, beef, and lamb.
- Preparation: The meat is usually marinated in a mixture of olive oil, lemon juice, and spices like oregano and garlic before being threaded onto skewers and grilled.
- Serving: Souvlaki is often served on the skewer for eating as is or removed from the skewer and served with pita bread, accompanied by sauces like tzatziki, and garnishes like sliced tomatoes and onions.
- Gyro:
- Ingredients: Gyro is made with meat cooked on a vertical rotisserie, traditionally pork or chicken, but also beef or lamb. The meat is typically seasoned with a blend of herbs and spices.
- Preparation: The meat is stacked in a cone-like shape and slowly cooked as it turns on the rotisserie. As it cooks, the outer layers are shaved off and continue to be cooked.
- Serving: Gyro is usually served as a sandwich, with the shaved meat wrapped in pita bread, along with ingredients like tomatoes, onions, lettuce, and tzatziki sauce.
Both souvlaki and gyro are staples in Greek cuisine and have become popular worldwide, with variations seen in different countries.
- Flavor and Texture:
- Souvlaki: The marination process gives souvlaki a distinct flavor, often with a noticeable hint of lemon and herbs. The grilling process provides a smoky flavor and a charred exterior while keeping the inside tender.
- Gyro: The slow cooking on the rotisserie makes gyro meat particularly tender and juicy. The herbs and spices used in the seasoning create a savory and sometimes slightly spicy flavor profile. The outer layer of the meat gets a bit crispy from the rotisserie’s heat.
- Cultural and Culinary Context:
- Souvlaki: This dish has ancient roots, with references dating back to ancient Greece. It’s a common street food in Greece and is often enjoyed as a quick and casual meal or snack.
- Gyro: The gyro is also a popular fast-food item in Greece and has a significant presence in Greek-American cuisine. The concept of cooking meat on a vertical rotisserie was likely inspired by the Turkish döner kebab and has similarities to the Middle Eastern shawarma.
- Health and Nutrition:
- Souvlaki: Depending on the meat used, souvlaki can be a lean and healthy option, especially when served with fresh vegetables and limited high-calorie sauces.
- Gyro: The meat in gyro can be more fatty, especially if it includes layers of fat to keep it moist during the cooking process. However, it can also be a good source of protein. The nutritional content also depends on the accompaniments and the amount of sauce used.
In summary, while both dishes feature grilled meat and are often accompanied by similar sauces and bread, souvlaki is characterized by its skewered and marinated chunks of meat, whereas gyro is known for its vertically rotisserie-cooked and shaved meat.